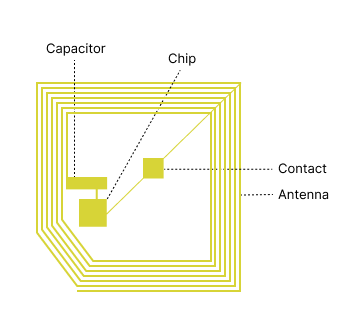
What is an RFID transponder?
An RFID transponder is a radio communication device. The transponder consists of a microchip and an antenna, which are housed in a small casing or, in the case of an RFID label, attached to a foil. The microchip stores information such as a serial number or any other unique ID. When the transponder is activated by an RFID reader, it sends the stored information to the reader via radio. RFID transponders are used in various applications, such as for identifying goods in logistics, for access control or for tracking objects in real time.
Energy supply for RFID transponders
There are three different types of power supply for RFID transponders:
![[Translate to English:] Aktive Transponder [Translate to English:] Aktive RFID-Transponder](/fileadmin/AutoID_RFID/rfid-tracking/aktive_transponder.png)
Active RFID transponders
These have their own energy source (battery), but are in idle mode until they receive an activation signal from a reader. This makes them suitable for longer ranges.
![[Translate to English:] Passive Transponder [Translate to English:] Passive RFID-Transponder](/fileadmin/AutoID_RFID/rfid-tracking/passive_transponder.png)
Passive RFID transponders
These do not require a battery and receive their energy from the reader via radio waves. They are cheaper, but only suitable for shorter distances. In addition, less information can be stored than with active tags.
![[Translate to English:] Semi-aktive Transponder [Translate to English:] Semi-aktive RFID-Transponder](/fileadmin/AutoID_RFID/rfid-tracking/semi-aktive_transponder.png)
Semi-active RFID transponders
They have a battery to support the electronics, but use the reader's energy for communication. They offer a medium range and efficiency.
Which transponders are used and when?
Transponders by technology
Transponders | Application | Description |
LF RFID transponder |
|
|
HF RFID transponder |
|
|
UHF RFID transponder |
|
|
Active RFID transponders |
|
|
RTLS tags |
|
|
Bluetooth tags (BLE) |
|
|
Transponder by type
Transponders | Application | Description |
RFID labels with paper and PET surface |
|
|
RFID labels with robust surface |
|
|
Transponder with special adhesive material |
|
|
On-metal RFID labels |
|
|
On-metal transponders/ hard tags |
|
|
Transponders for extreme environments |
|
|
Magnetic transponders |
|
|
Which transponders do we use?
We mainly use UHF transponders that comply with the EPC Gen 2 V1.2/ ISO 18000-6C standards, as well as transponders that are compatible with the 125 kHz and 13.56 MHz frequencies and the ISO 15693 and MIFARE Classic standards.
Checklist for choosing the right transponder
- What material should the transponder be made of? (e.g. plastic, metal, paper)
- What are the requirements regarding the durability, flexibility and chemical resistance of the material?
- Should the transponder be reusable or single-use?
- What purpose should the transponder fulfill (e.g. access control, warehouse management, product tracking)?
- In which sector will the transponder be used (e.g. logistics, production, retail)?
- How large is the free area available for the transponder?
From what distance must the transponder be able to be recognized by the reader? (close range, long range)
- Which environmental conditions are relevant? (e.g. temperature, humidity, dust, vibrations)
- Does the transponder need to be robust and weatherproof?
- How much data should be stored on the transponder? (e.g. serial number, product information)
How is the transponder integrated into your system? (e.g. existing ERP system, by means of middleware)
How do RFID transponders change the tracking of objects?
![[Translate to English:] Automatisierung [Translate to English:] Icon Automatisierung](/typo3conf/ext/sigma_template/Resources/Public/images/placeholder.png)
Automation
RFID allows objects to be identified automatically without the need for direct visual contact or manual input. This speeds up processes in areas such as warehousing, logistics and retail.
![[Translate to English:] Icon Echtzeit-Verfolgung [Translate to English:] Echtzeit-Verfolgung](/typo3conf/ext/sigma_template/Resources/Public/images/placeholder.png)
Real-time tracking
With RFID, objects can be tracked in real time as they move through a supply chain or production process. This enables precise location determination and improves transparency about their status.
![[Translate to English:] Datenerfassung mit RFID [Translate to English:] Icon Datenerfassung](/fileadmin/AutoID_RFID/rfid-tracking/RFID-Gate/funktionen_datenerfassung_icon.jpg)
Data acquisition
RFID transponders can contain additional information about an object, such as country of origin or production date. This data can be automatically recorded and integrated into company systems to improve traceability and quality control.
![[Translate to English:] Icon Sicherheit [Translate to English:] Diebstahlschutz und Sicherheit](/typo3conf/ext/sigma_template/Resources/Public/images/placeholder.png)
Theft protection and security
RFID can be used to protect objects from theft by triggering alarms when tagged objects are moved without authorization. This improves the security of inventory and valuables.
How does collected data help in decision-making?
Inventory management:
- Targeted ordering by recording information about stock levels
- Efficient planning of stock levels
- Targeted planning of sales (promotions)
Logistics and supply chain management:
- Tracking shipments and deliveries
- Optimization of the supply chain
- Real-time visibility of the flow of goods enables bottlenecks to be identified
- Planning of transportation and storage
Quality control:
- Tracking of products in the manufacturing process
- Decision-making for quality control and process optimization
Customer experience and marketing:
- Tracking customer interactions in retail
- Personalization of offers and marketing strategies
FAQ: The most frequently asked questions about RFID transponders
The reading range of RFID transponders varies depending on the type of transponder and the RFID technology used. Passive RFID transponders usually have a shorter read range (3 - 6 meters) compared to active transponders (more than 30 meters), as they do not have their own power supply and are therefore dependent on the energy of the reader. Active RFID transponders, which have their own battery, can offer a greater read range, which is particularly advantageous in applications where there is a greater distance between the reader and transponder. Factors such as the environment in which the RFID system is used and possible sources of interference can also influence the read range.
The battery life of active RFID transponders can vary depending on the manufacturer, model and use. As a rule, however, the batteries of active RFID transponders have a service life of 3 - 5 years before they need to be replaced or recharged. The exact lifespan depends on factors such as frequency of use, transmission range and environmental conditions.
The environment (e.g. metal, liquids), the reading distance, the frequency and the orientation of the transponder can influence the performance.
This depends on the type. Some transponders only have a few bytes for simple identification purposes, while others can store larger amounts of data, e.g. several kilobytes.
We will be happy to present solutions for your industry and your processes. Talk to the specialists for SMEs.
request now

